Understanding Mortgage Refinancing: A Complete Global Guide for Homeowners
Mortgage refinancing is one of the most effective financial strategies for reducing long-term housing costs, lowering monthly payments, accessing better interest rates, or unlocking home equity. Whether you are a homeowner in North America, Europe, Asia, or any other region, the fundamentals of refinancing remain similar: you replace your existing mortgage with a new one — often with better terms.
This complete global guide explains how mortgage refinancing works, when homeowners should consider it, the types of refinancing, benefits, risks, and strategies to maximize savings.
What Is Mortgage Refinancing?
Mortgage refinancing replaces your current home loan with a new one. The new loan pays off the existing mortgage, and you begin repaying under new terms such as interest rate, loan duration, or loan type.
Refinancing can help you:
- Lower your monthly mortgage payments
- Reduce your interest rate
- Tap into your home’s equity as cash
- Switch from variable to fixed rates (or vice versa)
- Shorten or extend your mortgage term
Why Homeowners Refinance
Across global markets, refinancing is most commonly done for:
- Lowering interest rates during economic downturns or market fluctuations
- Consolidating debt using home equity
- Freeing up monthly income by extending mortgage terms
- Financing home upgrades through cash-out refinance
- Switching loan types due to changing financial circumstances
Types of Mortgage Refinancing
1. Rate-and-Term Refinance
The most common type worldwide. This refinance changes the interest rate, repayment term, or both — without providing cash back.
2. Cash-Out Refinance
This allows homeowners to borrow against their home equity. The new mortgage is higher than the old one, and the difference is given as cash for:
- Home improvements
- Debt consolidation
- Education
- Emergency funds
- Real estate investments
3. Cash-In Refinance
Homeowners pay additional money toward the principal at closing to secure better terms or reduce overall interest costs.
4. Government-Assisted Refinancing (Varies by Country)
Many nations offer special refinancing programs for first-time buyers, low-income families, and veterans. Examples include:
- FHA Streamline (USA)
- VA IRRRL programs
- Government-backed refinance schemes in Canada, UK, Australia, India, Singapore, UAE, and others
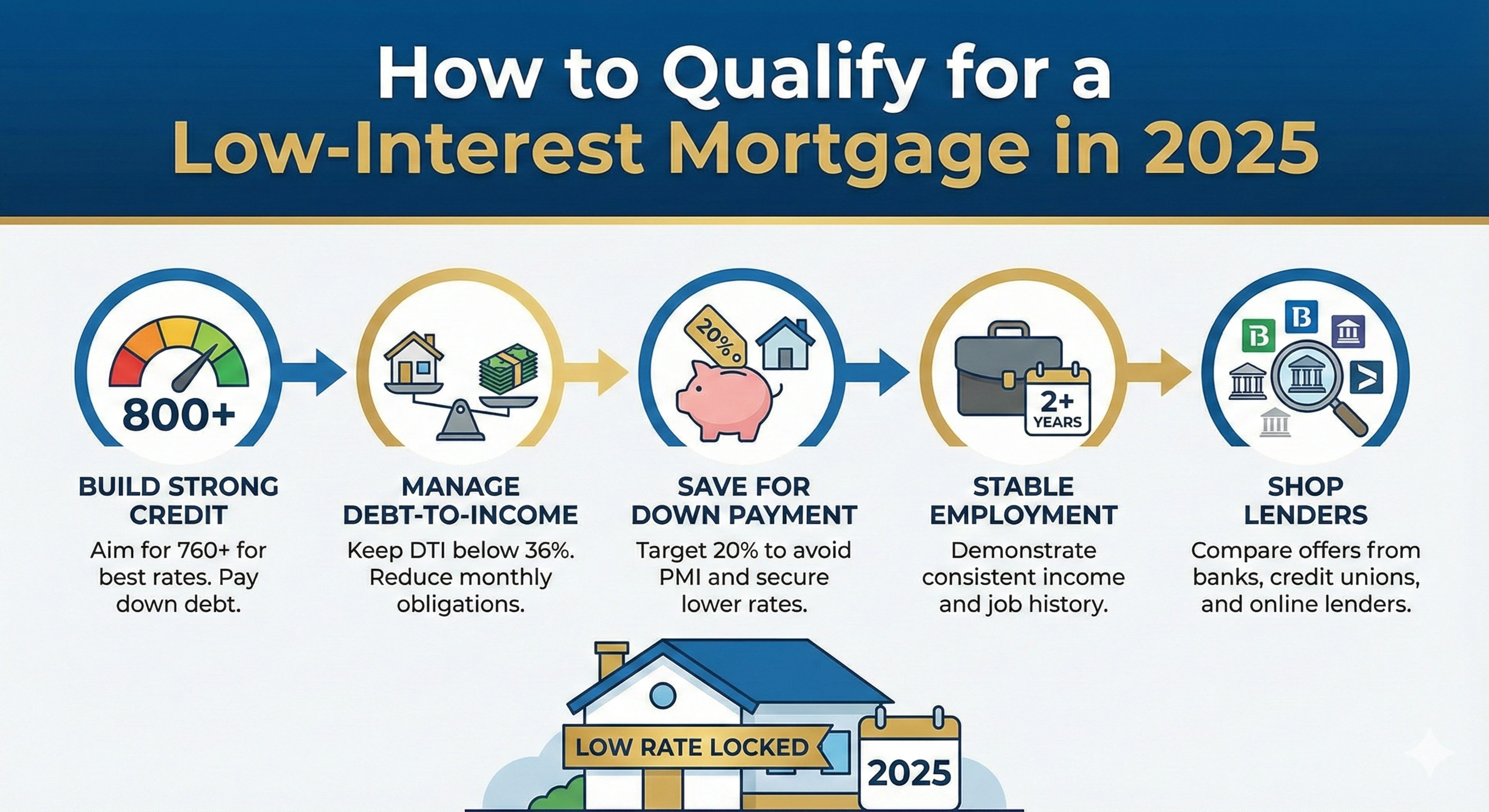
Eligibility Requirements
Although criteria vary across countries, these factors are universally required:
- Good credit score — Higher scores qualify for best rates
- Stable income — Verified through payslips, tax records, or business documents
- Low debt-to-income ratio — Typically under 40–45%
- Sufficient equity — Often at least 20%, though some markets allow lower
- Property appraisal — Determines home value and loan limits
Benefits of Refinancing
- Lower monthly payments
- Lower lifetime interest costs
- Ability to switch to stable fixed rates
- Opportunity to shorten mortgage length
- Cash-out access to home equity
- Better financial stability
Risks & Drawbacks
Refinancing isn’t always the best financial decision. Consider these risks:
- Closing costs (can be 2–5% of loan amount)
- Extending loan duration may increase long-term interest
- Variable rates may later rise
- Risk of overborrowing through cash-out refinance
- Qualification barriers if markets tighten
When Should You Refinance?
Globally, homeowners often refinance when:
- Interest rates drop by at least 0.5%–1%
- They require cash for major expenses
- They want to pay off the home faster
- Their credit has significantly improved
- Market conditions become more favorable
Refinancing vs HELOC vs Home Equity Loan
- Refinance: Best for lowering rates or withdrawing large amounts of equity.
- HELOC: Best for ongoing or unpredictable expenses.
- Home Equity Loan: Best for one-time fixed costs requiring predictable payments.
Step-by-Step Refinancing Process
- Evaluate your financial goals.
- Check credit scores and eligibility.
- Compare rates from multiple lenders.
- Calculate savings vs costs.
- Submit refinance application.
- Property appraisal and underwriting.
- Close the loan and begin new payments.
Tips to Maximize Savings
- Refinance early in the mortgage term if possible.
- Negotiate lender fees or ask for reductions.
- Optimize credit score before applying.
- Compare at least 4–6 lenders.
- Analyze break-even point before deciding.
Final Thoughts
Mortgage refinancing is a powerful financial tool when executed correctly. By securing better rates, restructuring debt, or leveraging equity for long-term value creation, homeowners worldwide can significantly improve their financial health. But timing, lender selection, and careful planning are crucial to ensuring it leads to real savings.
Understanding global refinancing trends and local lender policies helps homeowners make informed decisions that will benefit them for decades.
 Admin
Admin

 Admin
Admin