Understanding HELOC: A Complete Guide to Home Equity Lines of Credit
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) is one of the most flexible financial tools available to homeowners. By tapping into the equity built in your property, you can secure funds for home improvements, debt consolidation, education, medical expenses, or even investment opportunities. This guide provides a global, comprehensive understanding of HELOCs, how they work, and how to use them wisely.
1. What Is HELOC?
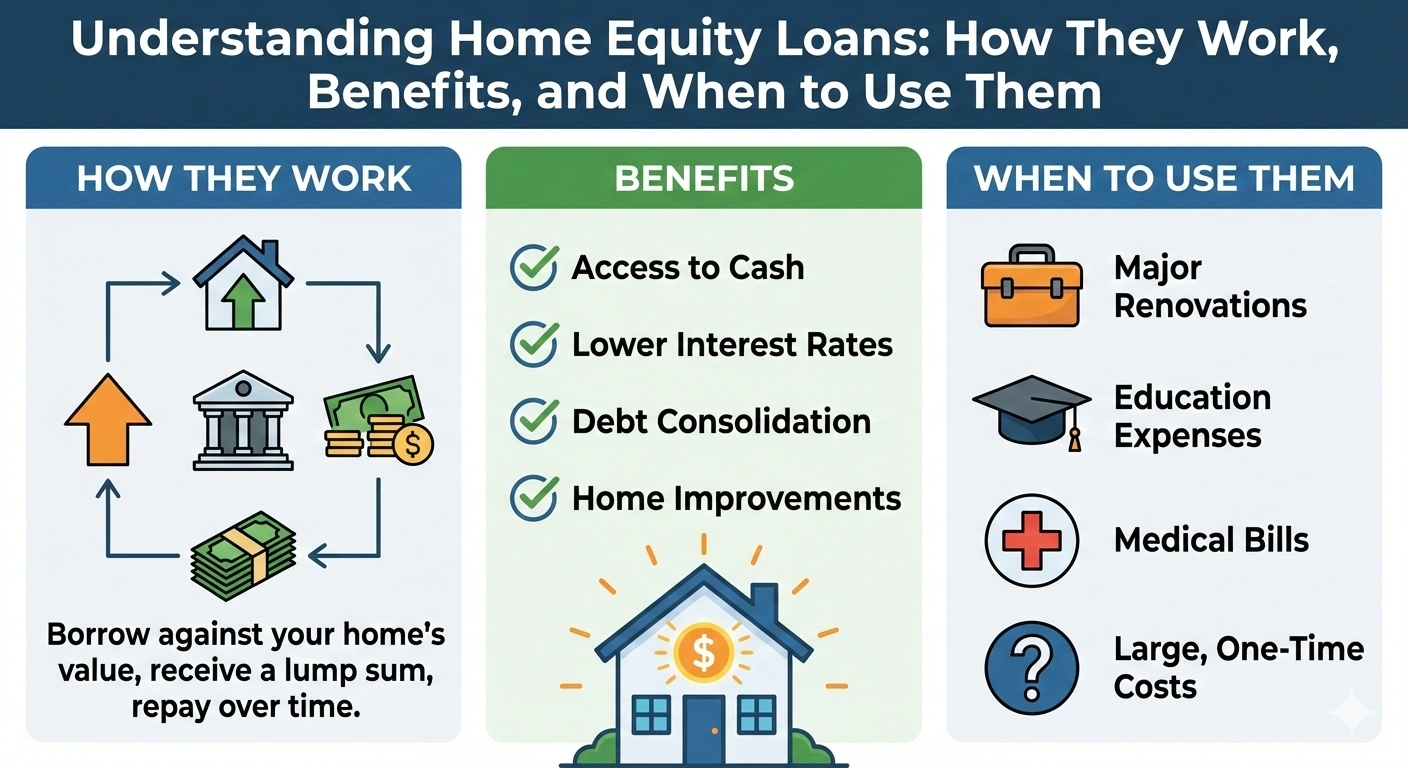
A HELOC is a revolving line of credit secured by your home equity. Instead of receiving a lump-sum loan, you get access to a credit line that you can borrow from as needed, similar to a credit card—but with much lower interest rates.
2. How Home Equity Is Calculated
Home equity is the difference between your home’s current market value and the outstanding mortgage balance. For example:
- Home value: $400,000
- Mortgage balance: $250,000
- Equity: $150,000
Lenders typically allow borrowers to access 60–85% of their property’s equity depending on the country and lender policies.
3. How HELOC Works
A HELOC has two main phases:
- Draw Period (5–10 years): You can borrow money anytime, up to the credit limit.
- Repayment Period (10–20 years): Borrowing stops and you repay principal + interest.
4. HELOC vs. Home Equity Loan vs. Cash-Out Refinance
- HELOC: Revolving credit line, flexible usage.
- Home Equity Loan: Lump sum with fixed interest.
- Cash-Out Refinance: Replaces your mortgage with a larger one and gives you the difference in cash.
5. Global Use Cases of HELOC
HELOC products vary across countries but are widely used for:
- Home renovation and upgrades
- Debt consolidation at lower interest
- Education or medical expenses
- Real estate investment
- Emergency liquidity
6. Advantages of a HELOC
- Lower interest rates compared to personal loans or credit cards
- Flexible borrowing—withdraw only what you need
- Interest-only payments possible during draw period
- No restrictions on fund usage
7. Risks of HELOC
While beneficial, HELOCs come with potential risks:
- Variable interest rates may increase over time
- Borrowing against your home increases foreclosure risk if you default
- You may overspend due to easy access to credit
- Your home value may decline, reducing equity
8. Requirements to Qualify for HELOC
Globally, lenders consider factors such as:
- Strong credit score
- Stable income and low debt-to-income ratio
- Sufficient home equity
- Verified property ownership
9. How to Use HELOC Wisely
- Borrow only for productive purposes
- Avoid unnecessary purchases
- Plan repayment ahead of time
- Monitor interest rate changes
- Compare lenders for best terms
10. Comparing HELOC Lenders
Before selecting a lender, compare:
- Interest rates (introductory vs. long-term)
- Fees (annual, withdrawal, appraisal, closing)
- Repayment flexibility
- Maximum credit limit
- Customer service quality
11. HELOC for Investment Opportunities
Some homeowners use HELOC funds to:
- Purchase rental properties
- Start or expand a business
- Invest in higher-return assets (cautiously)
12. When HELOC Is a Bad Idea
- If you have unstable income
- If you are planning to sell your home soon
- If you are consolidating debt without changing spending habits
- If interest rates are expected to rise significantly
Conclusion
HELOC can be a powerful financial tool for homeowners who use it responsibly. By understanding interest rates, repayment terms, risks, and global lender variations, you can make informed decisions and maximize the benefits of home equity.
 Admin
Admin

 Admin
Admin