Global HELOC Guide: How Homeowners Can Use Home Equity for Smarter Financial Planning
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) is one of the most flexible financial tools available to homeowners worldwide. Whether you live in North America, Europe, Asia, or emerging global markets, tapping into your home’s equity through a HELOC can help fund home improvements, consolidate debt, manage emergencies, or even support long-term investment strategies.
Unlike traditional loans, HELOCs allow homeowners to borrow money as needed, repay it, and borrow again — making them ideal for unpredictable expenses or multi-stage financial planning.
This comprehensive global HELOC guide covers everything homeowners need to know: how HELOCs work, qualification criteria, interest rates, pros, cons, strategies, alternatives, and smart ways to use home equity responsibly.
What Is a HELOC?
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) is a revolving credit line secured by your property. It works similarly to a credit card, but with a much lower interest rate because it’s backed by home equity.
How HELOCs Work
Homeowners receive access to a pool of funds based on the equity they have in their home. The HELOC typically has two phases:
- Draw Period (5–10 years): Homeowners can withdraw funds as needed.
- Repayment Period (10–20 years): Borrowers repay the balance through monthly payments.
Global Availability of HELOC Products
HELOCs are widely used in countries like:
- United States
- Canada
- United Kingdom (similar products: homeowner revolving credit)
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Hong Kong
- Singapore
- South Africa
In other regions such as India, UAE, and parts of the EU, similar products exist but may be offered under different names, such as top-up loans or property equity credit lines.
HELOC vs Home Equity Loan: What’s the Difference?
- HELOC: Revolving credit line with variable rates.
- Home Equity Loan: Lump sum with fixed rate and fixed repayment schedule.
HELOCs are ideal for ongoing or unpredictable expenses, while home equity loans suit one-time large expenses like medical bills, weddings, or major renovations.
How Much Home Equity Do You Need?
While limits vary globally, most lenders require homeowners to retain at least 15–25% of the home's value. Lenders generally allow borrowing up to 75–85% of the property’s market value.
Example
If your home is worth $300,000 and you owe $180,000, then:
Available Equity: $120,000
HELOC Limit (at 80% LTV): Up to $60,000–$75,000 depending on lender policies.
Requirements to Qualify for a HELOC
- Strong credit score
- Stable income and employment history
- Low debt-to-income (DTI) ratio
- Sufficient property equity
- Property appraisal and valuation
How HELOC Interest Rates Work
Most HELOCs use a variable interest rate tied to the country’s prime lending rate or interbank borrowing rate. This means your monthly payments may fluctuate.
Some lenders offer hybrid HELOCs or fixed-rate conversion options — allowing borrowers to lock in stable payments on part of their HELOC balance.
Benefits of a HELOC
- Flexible borrowing — withdraw when needed, repay anytime
- Lower interest rates than credit cards or personal loans
- Interest-only payments during draw period in some countries
- Reusable credit limit — borrow again after repayment
- Potential tax deductions (varies globally)
Drawbacks & Risks
- Variable rates may increase monthly payments
- Overborrowing risk
- Secured by your home — default may lead to foreclosure
- Closing costs may apply
- Property value fluctuations can affect equity
Smart Uses of a HELOC
1. Home Renovations
This is the most common and strategic use. Improvements typically increase property value, making it a smart investment.
2. Debt Consolidation
Homeowners worldwide use HELOCs to pay off high-interest debt like credit cards or personal loans.
3. Emergency Fund Backup
A HELOC provides instant access to capital during medical emergencies or major repairs.
4. Education Costs
Many global families use HELOCs for tuition fees, especially for overseas education.
5. Real Estate Investing
Leveraging home equity to acquire rental properties is gaining popularity across multiple regions.
6. Business Capital
Some business owners use HELOCs to fund new ventures or manage cash flow.
When Not to Use a HELOC
- High-risk investments
- Daily lifestyle expenses
- Luxury purchases
- If you expect a drop in home value
- If income stability is uncertain
Steps to Apply for a HELOC
- Check your credit score
- Evaluate your home’s market value
- Compare lenders globally and locally
- Prepare income and financial documents
- Submit application
- Undergo appraisal and underwriting
- Receive credit line and begin draw period
HELOC vs Refinance: Which Is Better?
- Choose a HELOC: For flexibility, ongoing expenses, or smaller borrowing needs.
- Choose Refinance: For major cash-out needs or lowering your rate.
Common Global HELOC Mistakes to Avoid
- Not comparing multiple lenders
- Borrowing without a repayment strategy
- Ignoring rate fluctuations
- Not verifying fees
- Using HELOC for depreciating assets
Future of HELOCs: Global Trends
As housing markets evolve, global HELOC products are expected to expand, especially in emerging nations where homeownership rates are rising. Digital lending, instant approvals, and AI-powered property valuation tools will further streamline HELOC applications.
Conclusion
HELOCs are powerful financial instruments that give homeowners worldwide flexibility and access to affordable credit. When used responsibly, they can support renovations, business growth, education, investment, and financial stability. However, because HELOCs are secured by your home, borrowers must analyze risks, compare lenders, and plan repayment carefully.
Understanding how HELOCs work globally empowers homeowners to make smarter financial choices and maximize the value of their property.
 Admin
Admin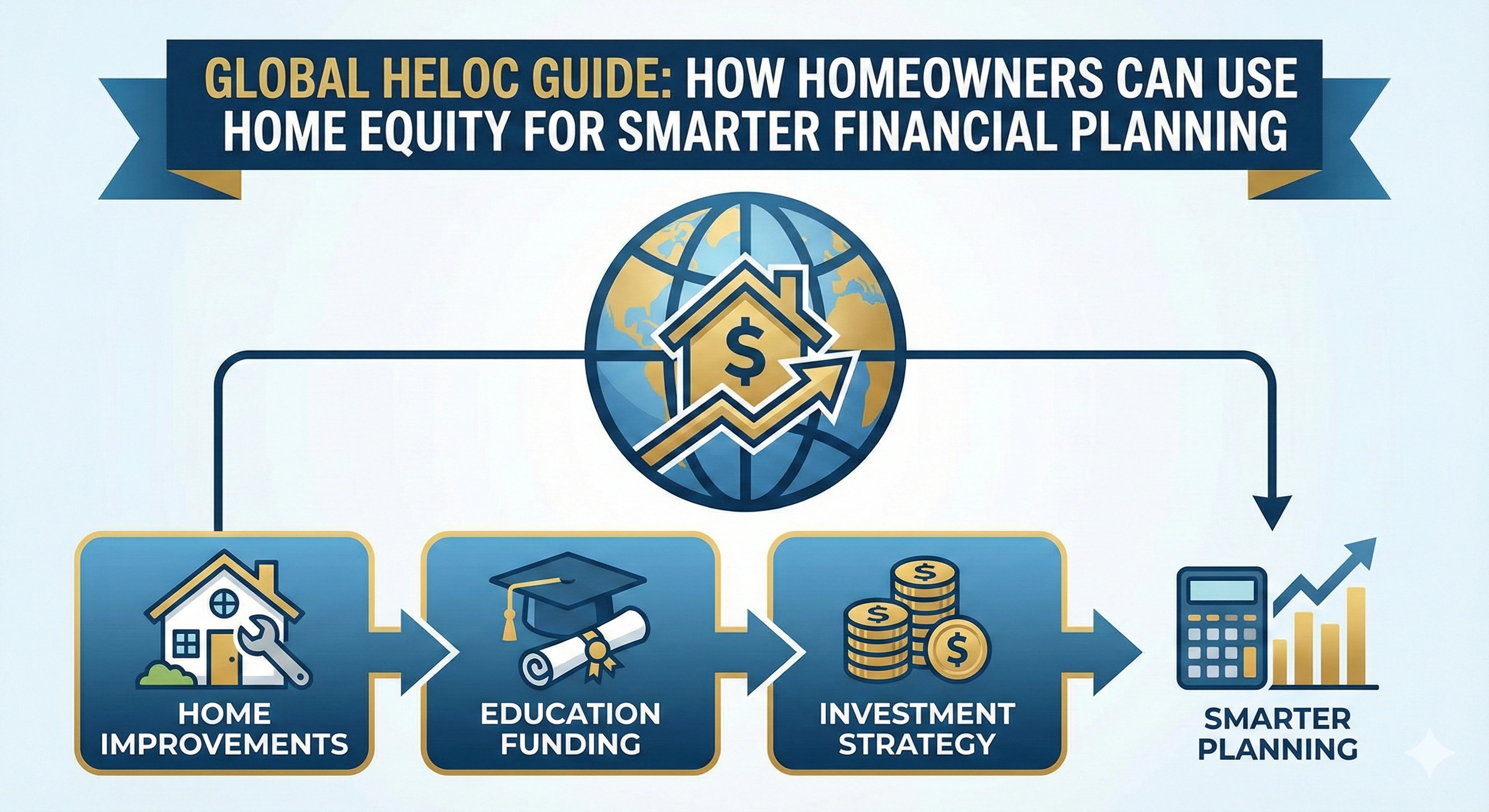

 Admin
Admin